
They should do so in the context of local and national priorities for funding and developing services, and in light of their duties to have due regard to the need to eliminate unlawful discrimination, to advance equality of opportunity and to reduce health inequalities. Local commissioners and providers of healthcare have a responsibility to enable the guideline to be applied when individual professionals and people using services wish to use it. It is not mandatory to apply the recommendations, and the guideline does not override the responsibility to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual, in consultation with them and their families and carers or guardian.Īll problems (adverse events) related to a medicine or medical device used for treatment or in a procedure should be reported to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency using the Yellow Card Scheme. When exercising their judgement, professionals and practitioners are expected to take this guideline fully into account, alongside the individual needs, preferences and values of their patients or the people using their service.
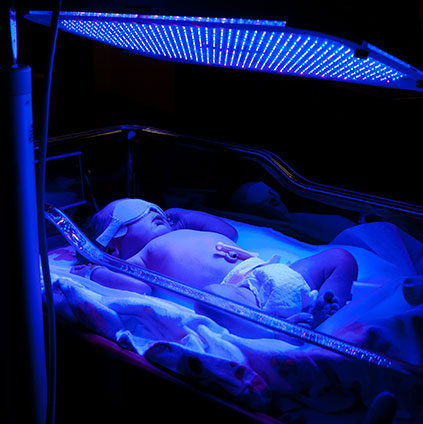
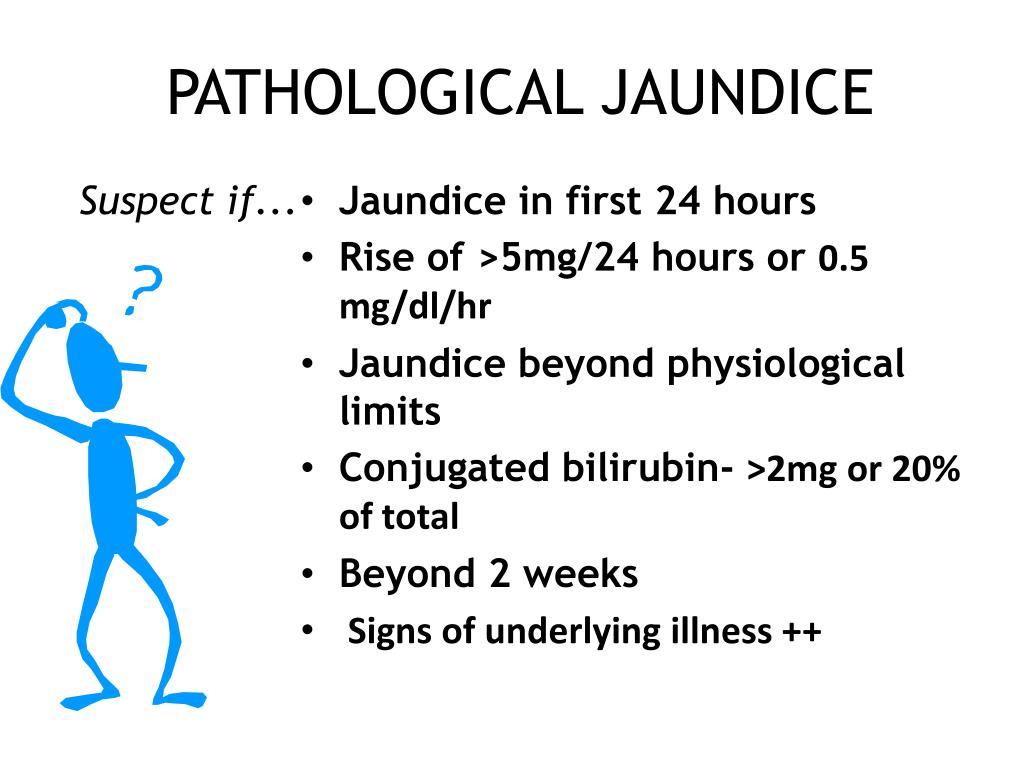
The recommendations in this guideline represent the view of NICE, arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available. PATHOLOGICAL JAUNDICE Etiology: The pathological jaundice appears in: » disorders of production » disorders of metabolism. We found no new evidence that affects the recommendations of this guideline. Parents of newborn babies and their families and carers.using intravenous immunoglobulin, exchange transfusion and other therapies.caring of babies with prolonged jaundice.assessing babies for underlying disease.measuring and monitoring bilirubin thresholds before and during phototherapy.managing and treating hyperbilirubinaemia.providing information to parents or carers.This guideline includes recommendations on: In October 2016, recommendation 1.4.9 was amended to clarify when intensified phototherapy should be used in relation to time since birth. It aims to help detect or prevent very high levels of bilirubin, which can be harmful if not treated. As soon as the baby is born and able to breathe oxygen the high Hb level is not needed and starts to drop. This is necessary during fetal life to facilitate oxygen carrying capacity. This guideline covers diagnosing and treating jaundice, which is caused by increased levels of bilirubin in the blood, in newborn babies (neonates). Jaundice A newborn baby has a haemoglobin (Hb) level of 18-19g/dl.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
